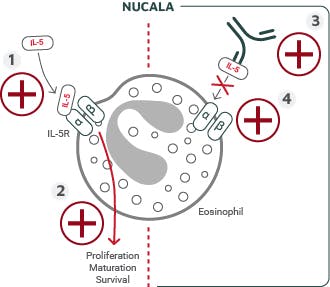
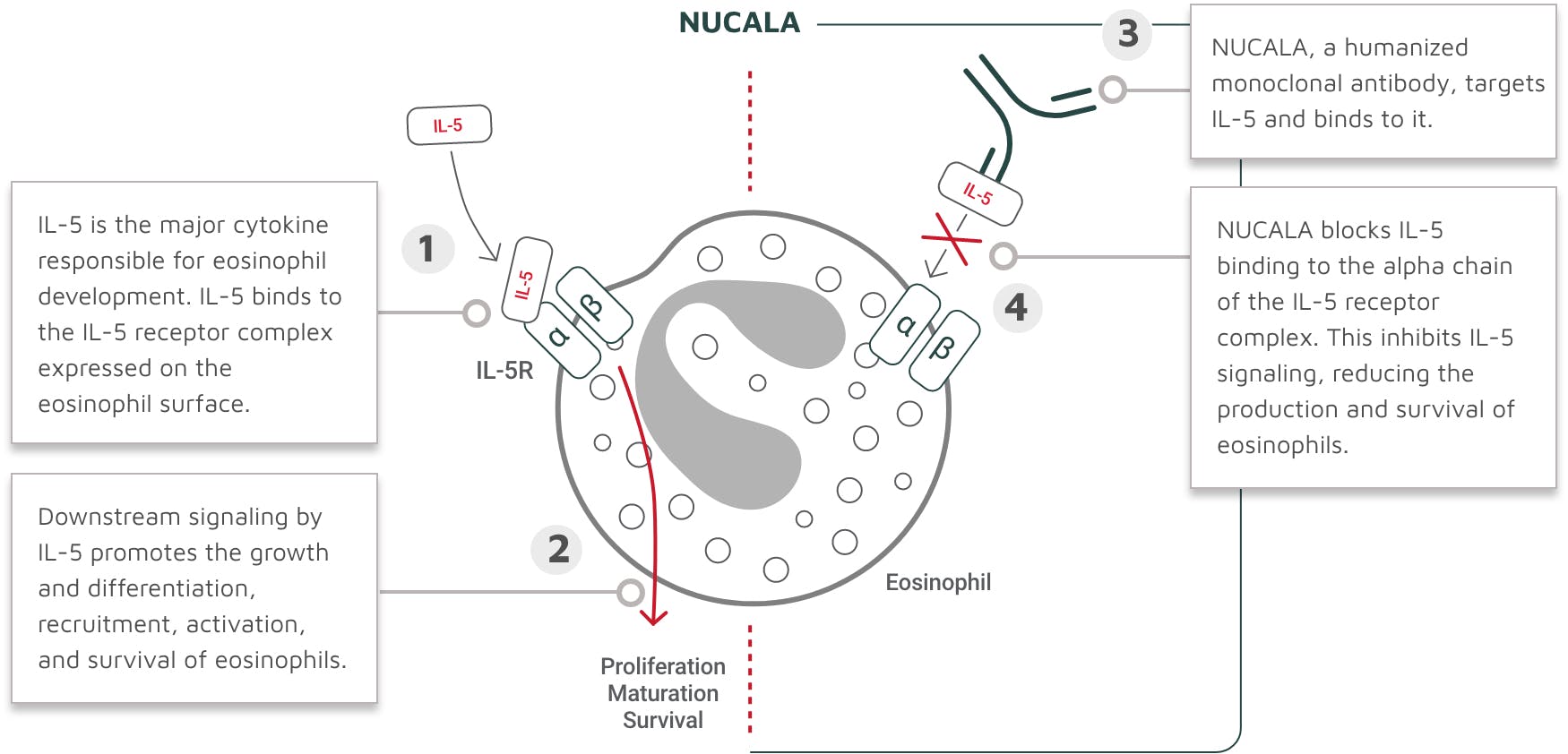
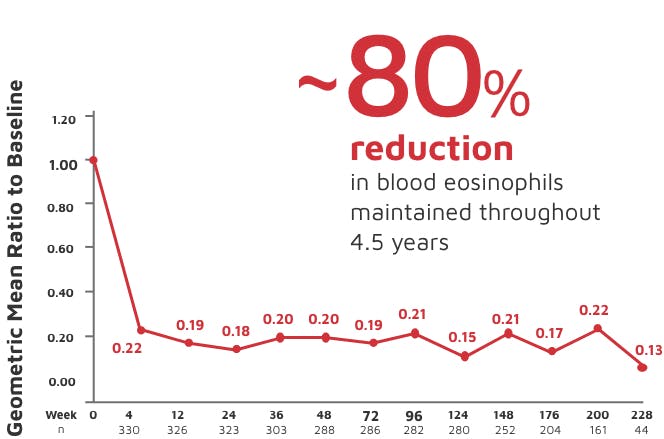
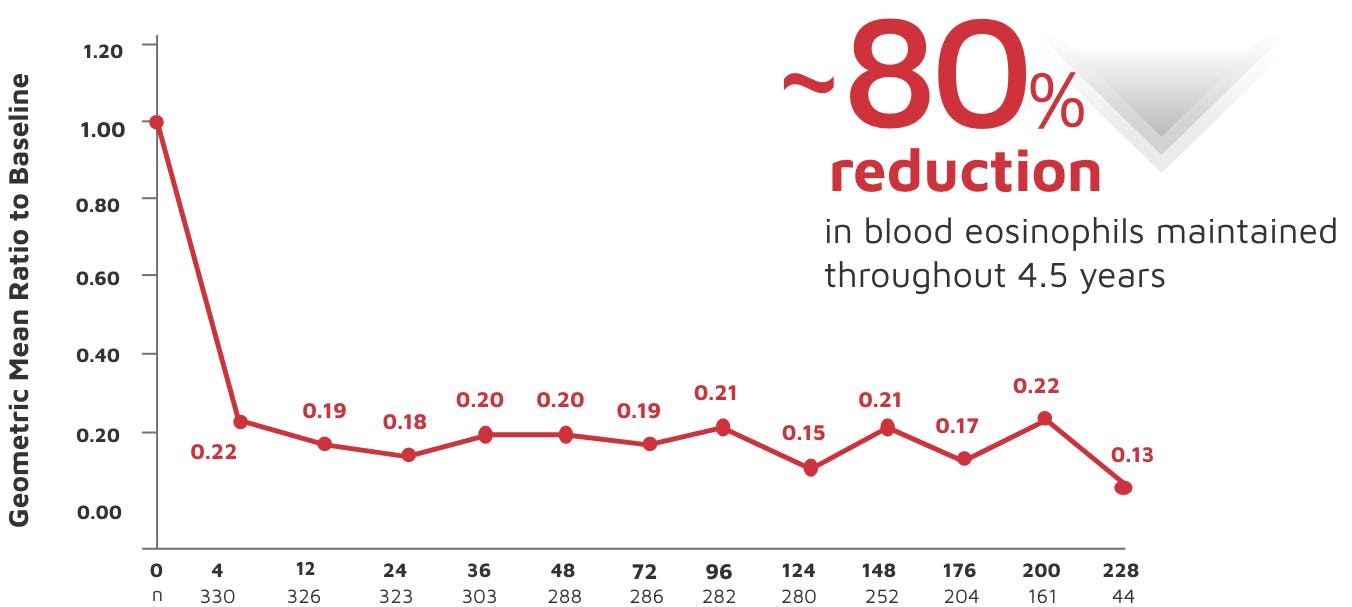
IL-5 is the major cytokine responsible for the growth and differentiation, recruitment, activation, and survival of eosinophils.
NUCALA is indicated for the add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with severe asthma and with an eosinophilic phenotype. NUCALA is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
NUCALA is indicated for the add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with severe asthma and with an eosinophilic phenotype. NUCALA is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
NUCALA is indicated for the add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with severe asthma and with an eosinophilic phenotype. NUCALA is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to mepolizumab or excipients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to mepolizumab or excipients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to mepolizumab or excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (eg, anaphylaxis, angioedema, bronchospasm, hypotension, urticaria, rash) have occurred with NUCALA. These reactions generally occur within hours of administration but can have a delayed onset (ie, days). Discontinue if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
Acute Asthma Symptoms or Deteriorating Disease
NUCALA should not be used to treat acute asthma symptoms, acute exacerbations, or acute bronchospasm.
Opportunistic Infections: Herpes Zoster
In controlled clinical trials, 2 serious adverse reactions of herpes zoster occurred with NUCALA compared to none with placebo. Consider vaccination if medically appropriate.
Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage
Do not discontinue systemic or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of therapy with NUCALA. Decreases in corticosteroid doses, if appropriate, should be gradual and under the direct supervision of a physician. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infection
Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with NUCALA. If patients become infected while receiving NUCALA and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue NUCALA until infection resolves.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In patients receiving NUCALA, the most common adverse reactions (≥5%) were headache, injection site reaction, back pain, and fatigue. Systemic reactions (allergic and nonallergic), including hypersensitivity, also occurred. Manifestations included rash, pruritus, headache, myalgia, and flushing; the majority were experienced the day of dosing.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
The data on pregnancy exposures are insufficient to inform on drug-associated risk. Monoclonal antibodies, such as mepolizumab, are transported across the placenta in a linear fashion as the pregnancy progresses; therefore, potential effects on a fetus are likely to be greater during the second and third trimesters.
Please see full Prescribing Information and Patient Information for NUCALA.
MPLWCNT230011 March 2023.